When you see something like 172.16.252.214.4300, it might look like a mysterious code, but it actually represents a combination of two important networking concepts: an IP address and a port number. Together, they form a key part of how devices communicate within private networks or internal systems.
In this detailed guide, we’ll explore what 172.16.252.214.4300 means, how it functions, why it matters in modern networking, and how you can troubleshoot or use such an address for testing, hosting, or network configuration.
1. Understanding the Basics: What Is an IP Address?
An IP address (Internet Protocol address) is a unique identifier assigned to every device connected to a network. It functions much like a street address for computers — allowing one device to locate and communicate with another across a network.
There are two main versions of IP addresses in use today:
-
IPv4: Example – 172.16.252.214.4300
-
IPv6: Example – 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
The address 172.16.252.214 falls under the IPv4 category, which is still the most widely used format worldwide.
2. Decoding 172.16.252.214.4300: Private IP Address Explained
The IP 172.16.252.214.4300 belongs to a range known as private IP addresses. These are not accessible directly from the internet — they are reserved for internal network communications.
According to the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), private IP address ranges include:
-
10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255
-
172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
-
192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255
So, 172.16.252.214 clearly fits within the 172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255 range, meaning it’s used for LANs (Local Area Networks) — not for external web servers or public sites.
These IPs are often used by companies, schools, or data centers for internal routing, virtual machines, and device communication.
3. What Does the “: 172.16.252.214.4300” Part Mean? Understanding Ports
Now, what about the “:4300” at the end?
That’s a port number, and it tells your device which service or application to connect to on that IP address.
Think of the IP as a building, and the port as a specific room within that building. Each port corresponds to a service.
Common examples include:
-
Port 80 → HTTP (web traffic)
-
Port 443 → HTTPS (secure web traffic)
-
Port 21 → FTP (file transfer protocol)
-
Port 25 → SMTP (email)
In this case, port 4300 is not a standard port. It’s considered a custom or dynamic port, possibly used by proprietary applications, local web servers, or development environments.
For example, a company might host an internal application or testing API at 172.16.252.214.4300 — accessible only to devices within that same private network.
4. Why Use Private IPs Like 172.16.252.214.4300?
Private IP addresses offer several key advantages in both enterprise and home environments:
a. Security
Private IPs are not reachable from the open internet, reducing exposure to cyber threats.
b. Resource Management
A single public IP can connect multiple private IPs through Network Address Translation (NAT), saving global IP space.
c. Internal Communication
Devices like printers, routers, and internal servers communicate efficiently using private IP addresses.
d. Local Testing
Developers often use private IPs for building and testing local web services before deployment.
So, 172.16.252.214.4300 could easily be a development server, IoT control panel, or database interface used only within an organization’s internal network.
5. Example Scenario: Accessing 172.16.252.214.4300
Imagine you’re a network engineer or developer in a company. The IT department gives you the URL:
When you type it into a browser on a computer connected to the same LAN, you might access an internal web dashboard or app.
But if you try it from your home Wi-Fi or mobile network, it won’t load — because the IP isn’t routable outside the organization.
This setup is very common for:
-
ERP or CRM systems
-
Employee portals
-
Local database dashboards
-
Smart device configuration pages
6. Common Issues When Accessing 172.16.252.214.4300
Sometimes, you might face problems when trying to connect to such private IPs. Here are the common causes:
a. Network Disconnection
You may not be connected to the same network as the private IP.
b. Firewall Restrictions
Firewalls may block access to certain ports like 4300 for security reasons.
c. Server Down
The service running on port 4300 may not be active or may have crashed.
d. Incorrect Port Mapping
If the NAT or routing table isn’t configured properly, your request won’t reach the target.
e. DNS or Proxy Issues
Local DNS servers or proxies might not recognize or forward the connection request.
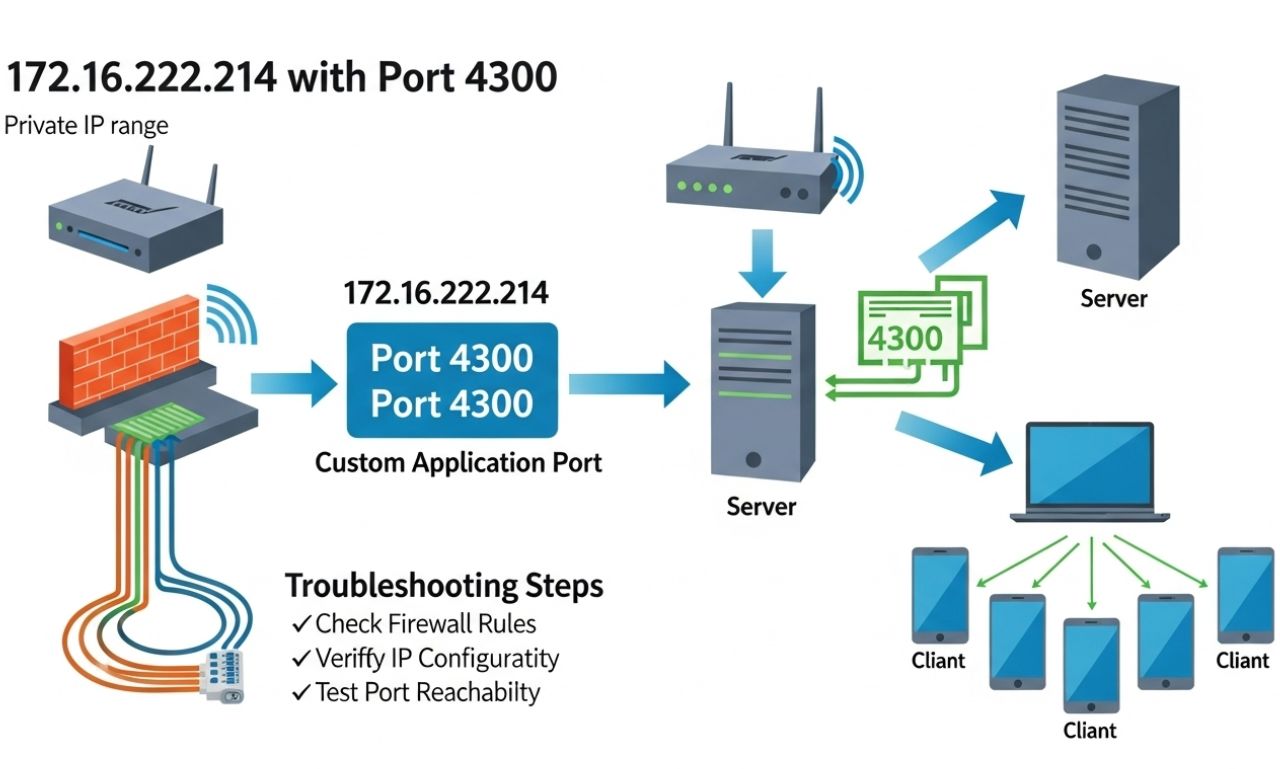
7. How to Troubleshoot 172.16.252.214.4300 Access Issues
If you’re unable to access the IP, here’s a step-by-step troubleshooting guide:
Step 1: Check Connectivity
Use the ping command:
If it responds, the host is online. If not, the connection may be blocked or unavailable.
Step 2: Verify Port Availability
Use Telnet or PowerShell:
If it connects, the port is open. If not, it’s likely closed or filtered by a firewall.
Step 3: Review Firewall Settings
Ensure that both the local and network firewalls allow inbound/outbound connections on port 4300.
Step 4: Check Application Status
Confirm that the service using port 4300 is actually running on the host device.
Step 5: Consult the IT Team
If the server is managed centrally, reach out to your IT department for access permissions.
8. The Role of Port 4300 in Networking
Port 4300 isn’t commonly assigned to standard internet protocols, but it’s often used in:
-
Custom TCP/UDP services
-
Internal APIs
-
Local web servers
-
IoT devices
-
Game servers
-
Development environments
In custom systems, developers often assign high-numbered ports (above 1024) to separate their services from well-known system ports.
9. Security Risks and Best Practices
Although private IPs like 172.16.252.214.4300 are not exposed to the internet, security misconfigurations can still cause problems.
Risks:
-
Unauthorized internal access
-
Malware spreading within the LAN
-
Exposed debug or admin panels
-
Weak or no authentication on internal services
Best Practices:
-
Implement strong internal passwords and authentication
-
Use VPN for remote access
-
Restrict unnecessary open ports
-
Regularly scan internal networks with tools like Nmap
-
Keep systems patched and updated
10. Advanced Insight: NAT and Port Forwarding
If you ever want to make 172.16.252.214.4300 accessible externally, you can configure Network Address Translation (NAT) or port forwarding on your router.
For example:
-
Your router’s public IP → 203.0.113.5
-
Internal IP → 172.16.252.214
-
Port → 4300
A forwarding rule can map:
However, this should only be done with caution, as it exposes the internal service to external traffic — which could create security vulnerabilities.
11. Use Cases of Private IP and Custom Ports
Here are some common real-world use cases for setups like 172.16.252.214.4300:
-
Intranet applications: Internal dashboards for employees.
-
Testing servers: Developers testing backend APIs.
-
IoT device control panels: Local servers for smart devices.
-
Educational labs: Virtual machines in university networks.
-
Database GUIs: Access interfaces for internal databases.
Each of these relies on private IPs and specific port assignments to ensure network efficiency and isolation.
12. FAQs About 172.16.252.214.4300
Q1. Is 172.16.252.214.4300 a public IP address?
No, it’s a private IP address within the 172.16.0.0/12 range, meant for internal network use.
Q2. Can I access 172.16.252.214.4300 from the internet?
Not directly. You’d need VPN access or proper port forwarding.
Q3. What is running on port 4300?
It could be any custom or internal application. You can identify it by checking local service configurations.
Q4. Is it safe to expose port 4300?
Only if protected with authentication, HTTPS, and strict access control.
Q5. Why can’t I open 172.16.252.214.4300 in my browser?
You might not be connected to the right network or the service might be down.
13. Conclusion: Why 172.16.252.214.4300 Matters
The address 172.16.252.214:4300 may seem like a random string, but in the world of networking, it’s a window into how computers communicate privately and securely.
It represents a private IP address (172.16.252.214.4300) combined with a specific service port (4300) — a common setup for internal tools, testing, and localized web applications.
Understanding private IPs like this helps IT professionals, developers, and cybersecurity experts manage networks more effectively, ensuring both performance and protection within local infrastructures.